If you’ve ever felt swelling of body parts seemingly out of nowhere, it can be both uncomfortable and frustrating. One of the common causes of this swelling is lymphedema.
Lymphedema manifests in different ways. It can even impact your vein health and, in turn, your physical well-being.
In this post, we’ll discuss the causes, symptoms, treatments, and misconceptions of lymphedema.
But wait – how does this relate to your veins?
Well, it’s an interesting relationship. But let’s start at the beginning:
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Lymphedema
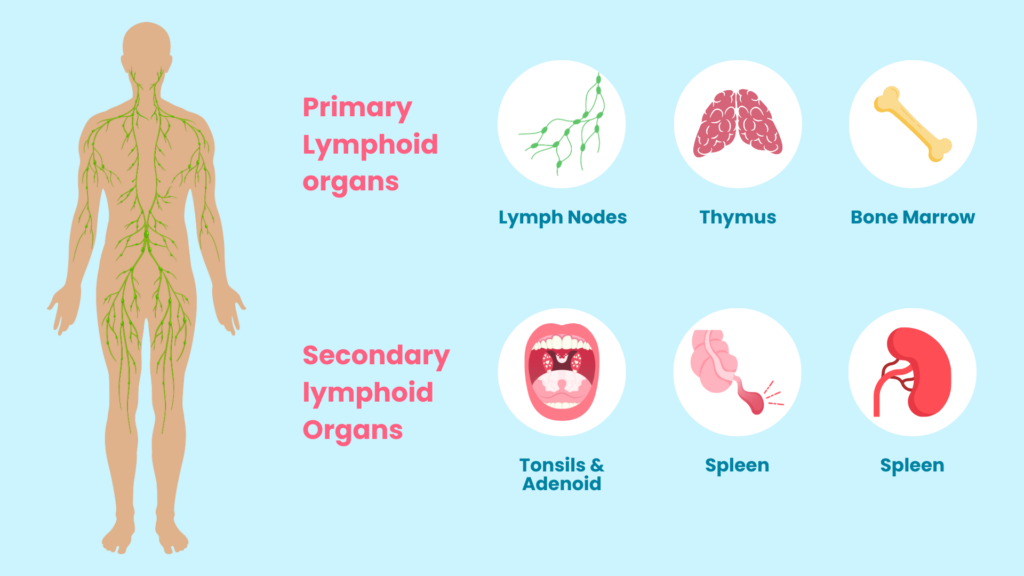
Your body has a lymphatic system. This is a part of your immune system.
Each system in your body plays an important role. The lymphatic system helps remove excess fluids and waste from your body.
When this system is compromised, fluids can accumulate. This leads to swelling in the arms or legs.
Lymphedema(1) is this swelling, and it is often a result of impaired lymphatic drainage.
Someone might first notice swelling of body parts, discomfort, and skin changes. You might also experience a “heavy” feeling in your limb(s) or a restricted range of motion(2).
Types of Lymphedema
There are two kinds of lymphedema: primary and secondary(3).
Primary lymphedema presents at birth or may develop later in life due to genetic factors(4). Any abnormalities in your lymphatic system are completely out of your control. Your body may naturally struggle to remove excess fluids.
Secondary lymphedema is much more common. This type also stems from damage to the lymphatic system(5), but this damage stems from:
- Surgery, such as lymph node removal
- Radiation therapy
- Infections
- Trauma
Cancer survivors have an increased risk of secondary lymphedema. Those with “venous insufficiency” – the improper functioning of leg veins – do as well.
Role of Veins in Lymphedema
Veins play a pivotal role in lymphedema and the lymphatic system. The venous and lymphatic systems are closely connected.
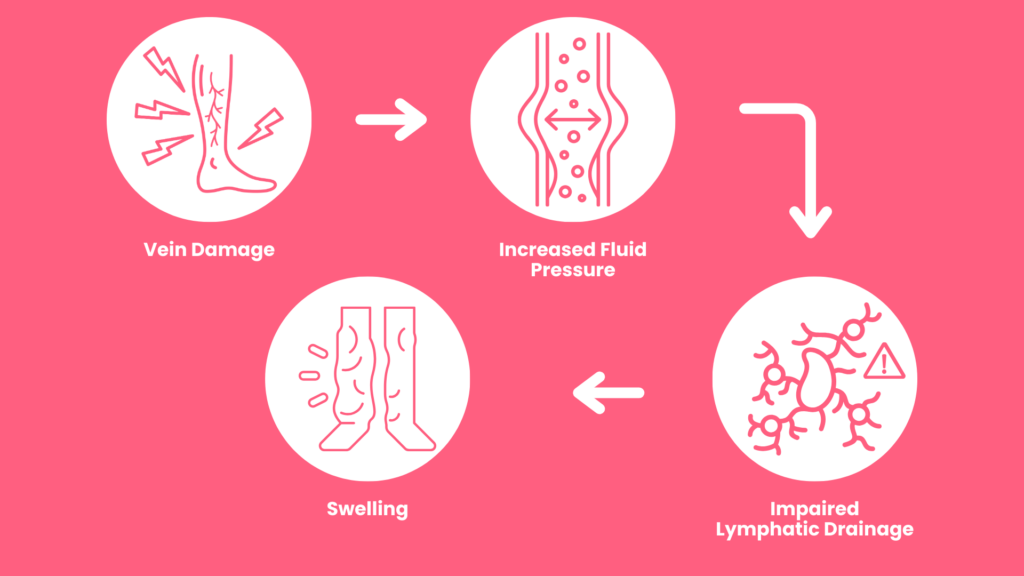
Lymphedema adds pressure on the vein, which impacts your blood circulation.
When veins struggle to perform, the fluid balance in your body is impacted. The lymphatic vessels, which work in tandem with veins, struggle to drain fluid from the body(6).
This swelling can further impede blood flow. This leads to conditions like venous insufficiency(7).
Common Vein Conditions and Lymphedema
You may have heard of terms such as varicose veins and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Let’s discuss how they affect the body:
Varicose veins(8) are enlarged, bulging veins that disrupt normal blood flow. This disruption affects the lymphatic system’s ability to manage fluids.
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when blood clots form in deep veins, causing discomfort. DVT can throw the entire circulatory system into disarray(9). These clots create a domino effect on lymphatic drainage.
These conditions indirectly affect the lymphatic vessels. This is due to the close relationship between the venous and lymphatic systems.
Strategies for Dealing with Varicose Veins and DVT
Patients with varicose veins can make lifestyle changes to help manage symptoms(10):
- Aiming for a healthy weight
- Regular exercise
- Avoid high heels
DVT, on the other hand, may need medical intervention. Certain medications can prevent further clotting(11). Your doctor can prescribe medication to help.
It’s essential to also focus on vein health while living with lymphedema.
Lymphedema Diagnosis
If you suspect you have lymphedema, here is how a diagnosis is reached(12):
Medical History and Physical Examination
First things first, talk to your doctor. Share all your symptoms. They will review your medical history and lifestyle.
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging helps detect blood flow issues, clots, or abnormalities in your veins. This step is crucial to find a connection between your veins and lymphatic vessels.
CT or MRI Scans
A doctor might recommend CT or MRI scans. These scans provide detailed images of the circulatory and lymphatic systems. They can help to spot structural issues and abnormalities.
Lymphoscintigraphy
The doctor will inject a small quantity of a radioactive substance into the body. This helps trace fluid movement and assess blood flow (13).
Venography
With a larger vein, the doctor injects a contrasting dye, making it visible on X-rays(14). The doctor can then look inside the vein structure and identify any abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Lymphedema
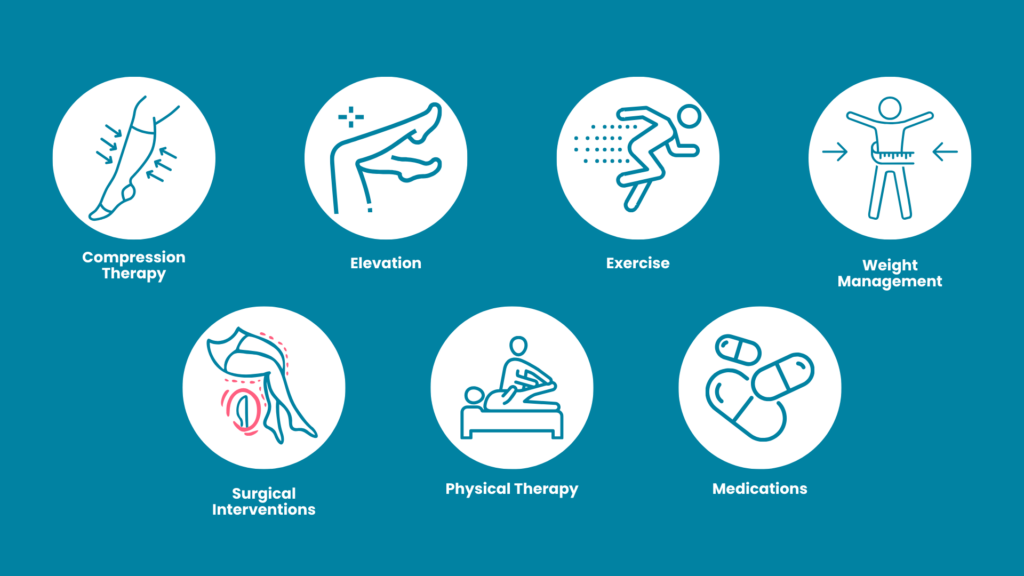
Lymphedema can be uncomfortable, but it is manageable. Here are nine ways to better manage your symptoms and treat the condition:
Compression Therapy
Specialized stockings or bandages apply gentle pressure to help veins perform efficiently (15). This external support to veins and lymphatic vessels helps reduce swelling.
Elevation
Lift your legs up! By elevating your limbs, you’re helping blood and lymphatic fluid to return to the heart. This is great after prolonged sitting or standing.
Exercise
Regular physical activity enhances circulation and reduces swelling while also promoting overall health. It’s a win-win!
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential when living with lymphedema. Extra weight can put undue pressure on veins, worsening lymphedema. Eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly helps.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
MLD is a massage tailored for your lymphatic system. Therapists use gentle, rhythmic movements to stimulate lymphatic drainage(16).
Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT)
CDT is a combination of techniques used to manage lymphedema. This therapy regimen includes MLD, compression therapy, exercise, and skincare(17).
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is sometimes necessary to remove excess tissue or repair damaged veins. Some patients may need a lymph node transplant(18). The best type of surgical treatment will vary from person to person.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy enhances muscle strength, joint flexibility, and bodily function.
Medications
Your doctor might prescribe medications like diuretics or anticoagulants. These can help to manage symptoms or prevent complications(19).
Treatment for lymphedema is not one size fits all. Your healthcare provider will tailor a plan based on your specific challenges.
Lymphedema and Quality of Life
Beyond its symptoms, lymphedema can impact your quality of life. Do not underestimate the emotional toll of living with a chronic condition.
Physical Limitations
Lymphedema can impose physical limitations on daily activities. Routine tasks may become more challenging due to restricted movement. Occupational therapy and adaptive strategies can help increase independence and improve well-being.
Emotional Impact
Dealing with visible swelling may lead to reduced self-esteem and feelings of self-consciousness. You might experience anxiety or depression as you navigate the challenges of managing lymphedema(2).
The following practices can contribute to a positive mindset(21):
- Engaging in hobbies and fun activities
- Practicing mindfulness
- Seeking support through community groups
Myths and Facts
There are some common misconceptions about lymphedema:
I thought this only affects older adults – it won’t affect me.
If I had lymphedema, it’d be evident with the swelling.
Why did you recommend exercise – doesn’t it make it worse?
Let’s take a second to debunk some myths surrounding vein health and lymphedema:
Myth: Lymphedema is Always Caused by Cancer
Fact: Cancer-related treatments can contribute to lymphedema. But this condition has several other causes, including genetic factors and infections(22).
Myth: Lymphedema is Always Visible
Fact: Lymphedema can manifest as visible swelling, but you may only experience discomfort or a “heaviness” feeling(23).
Myth: Lymphedema is Untreatable
Fact: There are several effective management strategies for lymphedema. Some examples include(24):
- Compression therapy
- Manual lymphatic drainage
- Surgical interventions
Myth: Exercise Worsens Lymphedema
Fact: The right exercises can alleviate symptoms and improve lymphatic function(25).
Myth: Only Women Get Lymphedema
Fact: Breast cancer-related lymphedema is well-known, but men can also develop lymphedema. It can occur in any body part and is not exclusive to a particular gender(26).
Myth: Only Older Adults Experience Vein Issues.
Fact: Vein conditions can affect people of all ages(2). Age may increase your risk, but lifestyle factors, genetics, and other elements play a big role.
Compression Stockings Are Uncomfortable and Unstylish.
Fact: Modern compression socks come in various styles, colors, and pressure levels(28).. Chances are there is a pair out there that fits your style!
Conclusion
A health problem is not often isolated to one part of the body. Lymphedema and its ties to vein conditions are a clear example. It’s a multifaceted journey!
But now you’ve familiarized yourself with lymphedema and its ties to vein health. Education is power, and you’re now empowered to make better decisions for your health and seek the help you need.
When it’s time to get your vein health under control, Elite Vein Clinic is here for you. One of our experts will evaluate your symptoms and medical history and determine the best treatment plan for you with a patient-first approach and the latest medical technology. Find our offices in Phoenix, Chandler, Gilbert, Mesa, Scottsdale, Tempe, and Peoria.
Take the first step toward a healthier you. Book your free consultation today!
References
1. https://medlineplus.gov/lymphedema.html
2. https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/lymphoedema
3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537239
4. Brouillard P, Witte MH, Erickson RP, Damstra RJ, Becker C, Quéré I, Vikkula M. Primary lymphoedema. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021 Oct 21;7(1):77. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00309-7. PMID: 34675250.
5. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780323298971000061
6. Vaqas B, Ryan TJ. Lymphoedema: Pathophysiology and management in resource-poor settings – relevance for lymphatic filariasis control programmes. Filaria J. 2003 Mar 12;2(1):4. doi: 10.1186/1475-2883-2-4. PMID: 12685942; PMCID: PMC153482.
7. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000203.htm
8. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/circulationaha.113.008331
9. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis-dvt/
10. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/varicose-veins
12. Greene AK, Goss JA. Diagnosis and Staging of Lymphedema. Semin Plast Surg. 2018 Feb;32(1):12-16. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1635117. Epub 2018 Apr 9. PMID: 29636648; PMCID: PMC5891654.
13. Villa G, Campisi CC, Ryan M, Boccardo F, Di Summa P, Frascio M, Sambuceti G, Campisi C. Procedural Recommendations for Lymphoscintigraphy in the Diagnosis of Peripheral Lymphedema: the Genoa Protocol. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Feb;53(1):47-56. doi: 10.1007/s13139-018-0565-2. Epub 2019 Jan 7. PMID: 30828401; PMCID: PMC6377575.
14. https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(11)01833-7/fulltext
18. Kareh AM, Xu KY. Surgical Management of Lymphedema. Mo Med. 2020 Mar-Apr;117(2):143-148. PMID: 32308240; PMCID: PMC7144713.
19. Pal S, Rahman J, Mu S, Rusch NJ, Stolarz AJ. Drug-Related Lymphedema: Mysteries, Mechanisms, and Potential Therapies. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 4;13:850586. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.850586. PMID: 35308247; PMCID: PMC8930849.
20. Fu MR, Ridner SH, Hu SH, Stewart BR, Cormier JN, Armer JM. Psychosocial impact of lymphedema: a systematic review of literature from 2004 to 2011. Psychooncology. 2013 Jul;22(7):1466-84. doi: 10.1002/pon.3201. Epub 2012 Oct 9. PMID: 23044512; PMCID: PMC4153404.
21. https://www.harvard.edu/in-focus/mindfulness-meditation/
22. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537239/
23. https://www.healthline.com/health/lymphatic-obstruction
24. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/lymphoedema/treatment
25. Morris C, Wonders KY. Concise review on the safety of exercise on symptoms of lymphedema. World J Clin Oncol. 2015 Aug 10;6(4):43-4. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v6.i4.43. PMID: 26266100; PMCID: PMC4530377.
26. Morfoisse F, Zamora A, Marchaud E, Nougue M, Diallo LH, David F, Roussel E, Lacazette E, Prats AC, Tatin F, Garmy-Susini B. Sex Hormones in Lymphedema. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 30;13(3):530. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030530. PMID: 33573286; PMCID: PMC7866787.
27. Studennikova VV, Severgina LO, Dzyundzya AN, Korovin IA. Mekhanizmy razvitiia i osobennosti varikoznoĭ bolezni ven nizhnikh konechnosteĭ v detskom i molodom vozraste [Lower extremity varicose veins in childhood and at a young age: Mechanism of development and specific features]. Arkh Patol. 2017;79(4):56-60. Russian. doi: 10.17116/patol201779456-60. PMID: 28792000.
28. https://www.cnet.com/health/fitness/best-compression-socks/